Palmitic acid, a saturated fat concentrated in meat and dairy, can boost the metastatic potential of cancer cells through the fat receptor CD36.
The leading cause of death in cancer patients is metastasis formation. That’s how most people die of cancer—not from the primary tumor, but the cancer spreading through the body. “It is estimated that metastasis is responsible for ~90% of cancer deaths,” and little progress has been made in stopping the spread, despite our modern medical armamentarium. In fact, we can sometimes make matters worse. In an editorial entitled “Therapy-Induced Metastasis,” its authors “provide evidence that all the common therapies, including radiotherapy, chemotherapy, fine needle biopsies, surgical procedures and anaesthesia, have the potential to contribute to tumour progression.” You can imagine how cutting around a tumor and severing blood vessels might lead to the “migration of residual tumour cells,” but why chemotherapy? How might chemo exacerbate metastases? “Despite reducing the size of primary tumors, chemotherapy changes the tumor microenvironment”—its surrounding tissues—“resulting in an increased escape of cancer cells into the blood stream.” Sometimes, chemo, surgery, and radiation are entirely justified, but, again, other times, these treatments can make matters worse. If only we had a way to treat the cause of the cancer’s spreading.
The development of antimetastatic therapies has been hampered by the fact that the cells that initiate metastasis remain unidentified. Then, a landmark study was published: “Targeting Metastasis-Initiating Cells Through the Fatty Acid Receptor CD36.” Researchers found a subpopulation of human cancer cells “unique in their ability to initiate metastasis”; they all express high levels of a fat receptor known as CD36, dubbed “the fat controller.” It turns out that palmitic acid or a high-fat diet specifically boosts the metastatic potential of these cancer cells. Where is palmitic acid found? Although it was originally discovered in palm oil, palmitic acid is most concentrated in meat and dairy. “Emerging evidence shows that palmitic acid (PA), a common fatty acid in the human diet, serves as a signaling molecule regulating the progression and development of many diseases at the molecular level.” It is the saturated fat that is recognized by CD36 receptors on cancer cells, and we know it is to blame, because if the CD36 receptor is blocked, so are metastases.
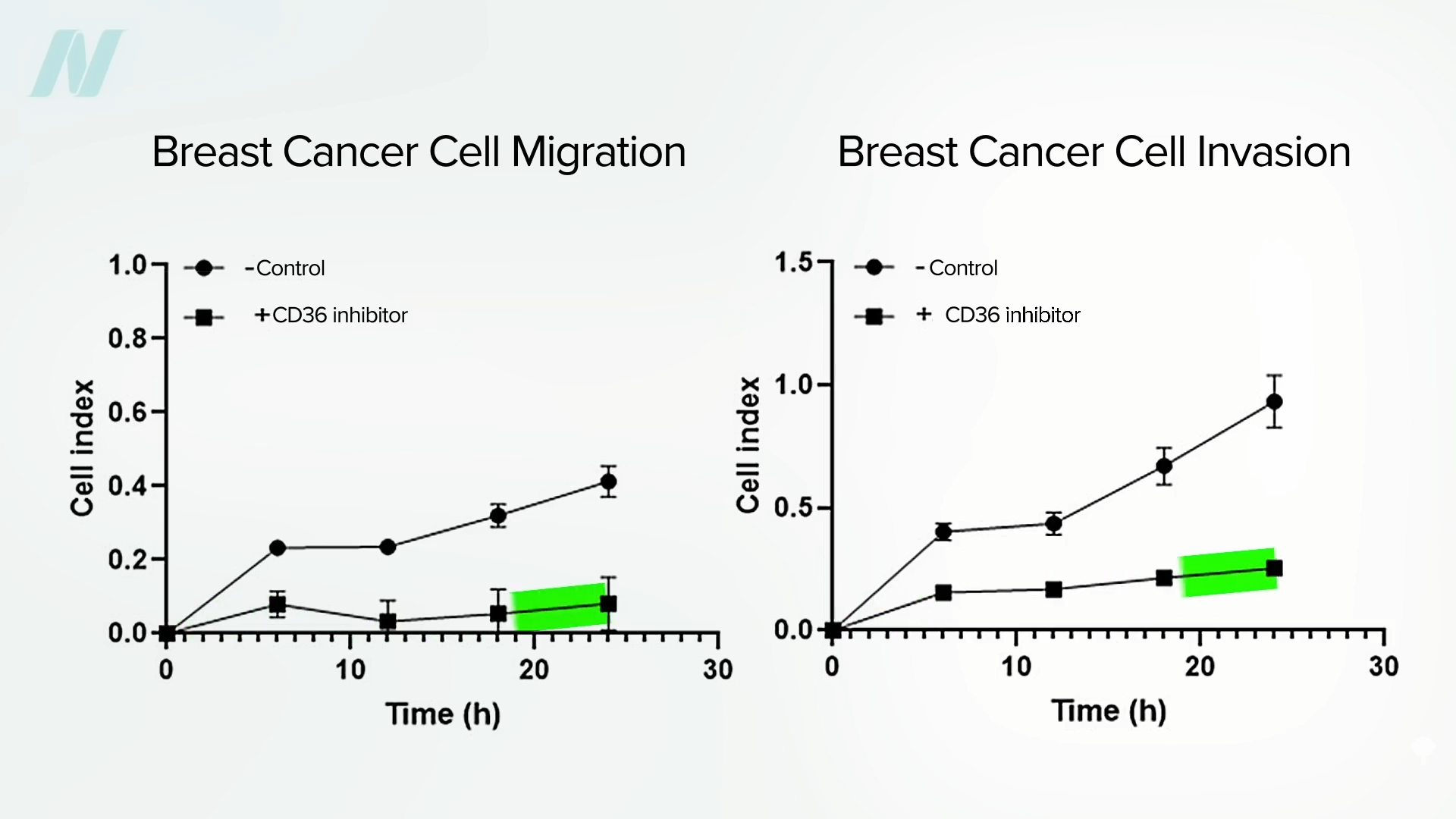
The study was of a human cancer, but it was a human cancer implanted into mice. However, clinically (meaning in cancer patients themselves), the presence of these CD36-studded metastasis-initiating cells does indeed correlate with a poor prognosis. CD36 appears to drive the progression of brain tumors, for example. As seen in the survival curves shown below and at 3:21 in my video What Causes Cancer to Metastasize?, those with tumors with less CD36 expression lived significantly longer. It is the same with breast cancer mortality: “In this study, we correlated the mortality of breast cancer patients to tumor CD36 expression levels.” That isn’t a surprise, since “CD36 plays a critical role in proliferation, migration and…growth of…breast cancer cells.” If we inhibit CD36, we can inhibit “the migration and invasion of the breast cancer cells.”
Below and at 3:46 in my video, you can see breast cancer cell migration and invasion, before and after CD36 inhibition. (The top lines with circles are before CD36 inhibition, and the bottom lines with squares are after.)
This isn’t only in “human melanoma- and breast cancer–derived tumours” either. Now we suspect that “CD36 expression drives ovarian cancer progression and metastasis,” too, since we can inhibit ovarian cancer cell invasion and migration, as well as block both lymph node and blood-borne metastasis, by blocking CD36. We also see the same kind of effect with prostate cancer; suppress the uptake of fat by prostate cancer cells and suppress the tumor. This was all studied with receptor-blocking drugs and antibodies in a laboratory setting, though. If these “metastasis-initiating cancer cells particularly rely on dietary lipids [fat] to promote metastasis,” the spread of cancer, why not just block the dietary fat in the first place?
“Lipid metabolism fuels cancer’s spread.” Cancer cells love fat and cholesterol. The reason is that so much energy is stored in fat. “Hence, CD36+ metastatic cells might take advantage of this feature to obtain the high amount of energy that is likely to be required for them to anchor and survive at sites distant from the primary tumour”—to set up shop throughout the body.
“The time when glucose [sugar] was considered as the major, if not only, fuel to support cancer cell proliferation is over.” There appears to be “a fatter way to metastasize.” No wonder high-fat diets (HFD) may “play a crucial role in increasing the risk of different cancer types, and a number of clinical studies have linked HFD with several advanced cancers.”
If dietary fat may be “greasing the wheels of the cancer machine,” might there be “specific dietary regimens” we could use to starve cancers of dietary fat? You don’t know until you put it to the test, which we’ll look at next.